-
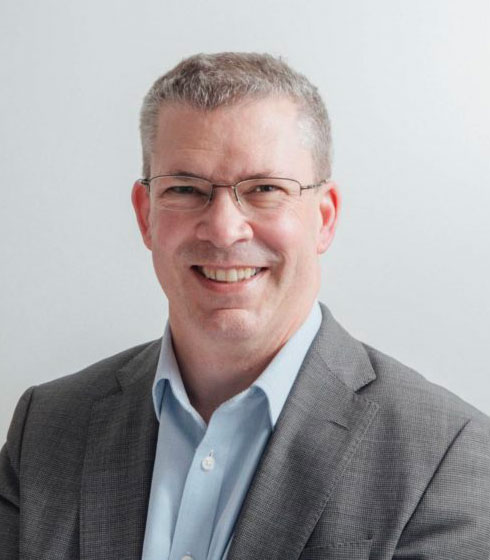

NHS Supply Chain appoints new Chair of NHS Advisory Board for Procurement and Supply
•
Joe Harrison CBE, Chair of the NHS Advisory Board for Procurement and Supply at NHS Supply Chain Joe Harrison CBE has been appointed by NHS Supply Chain as Chair of the NHS Advisory Board for Procurement and Supply, effective immediately. The NHS Advisory Board for Procurement and Supply (The National Advisory Board) aims to…
-
-
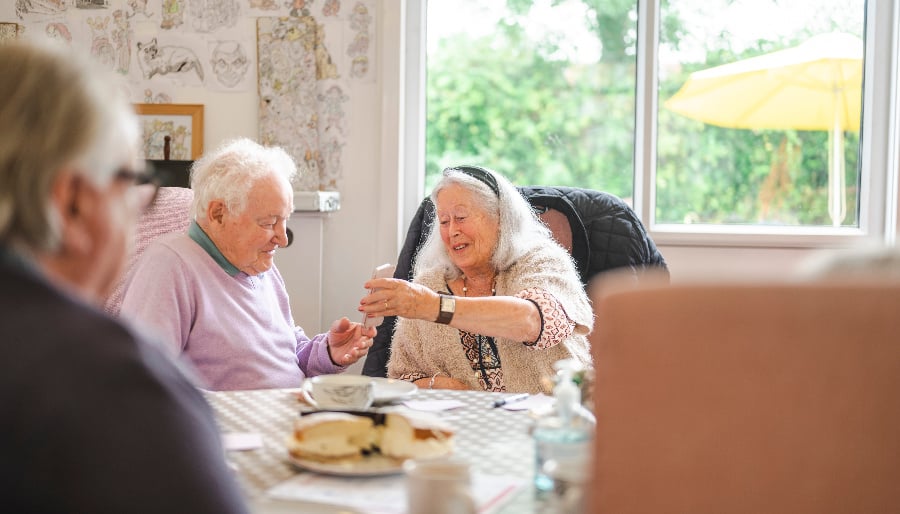

HSCP receives recognition for the completion of its analogue to digital telecare transition project
•
The Digital Office for Scottish Local Government has awarded Inverclyde Health and Social Care Partnership (HSCP) the Platinum Digital Telecare Implementation Award in recognition of the recent completion of its analogue to digital telecare transition project. To achieve Platinum, a telecare service provider must have successfully rolled out a live digital telecare service to…
-

Video: Telecare users across the UK urged to speak to telecoms providers ahead of digital switchover
•
A national awareness campaign has been launched by BT and Virgin Media that urges the two million telecare users in the UK to get in touch with their landline providers so companies can provide additional support for them during the switch to digital landlines. Backed by the UK Government, the major campaign is designed…
-
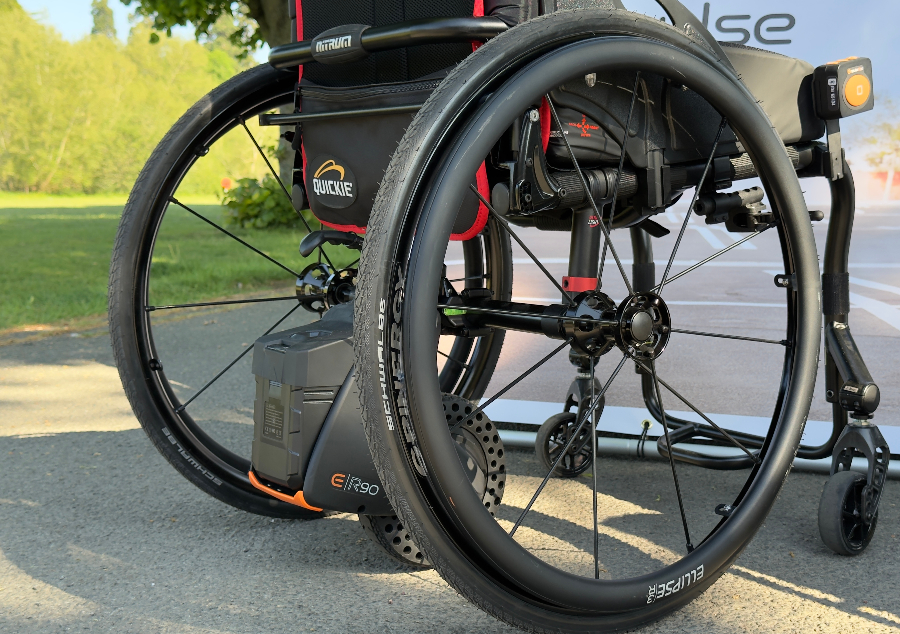

Mobility solutions provider launches seven new products that enhance accessibility
•
Mobility solutions provider Sunrise Medical has unveiled seven new products, designed to revolutionise mobility solutions at its Elite Dealer launch event. Hosted at Warwickshire Walton Hall Hotel & Spa, the event featured the latest mobility solutions from Sunrise Medical’s Magic Mobility, Empulse, Sterling and Quickie brands, with over 100 prescribers attending from 40 Elite retailers…
-
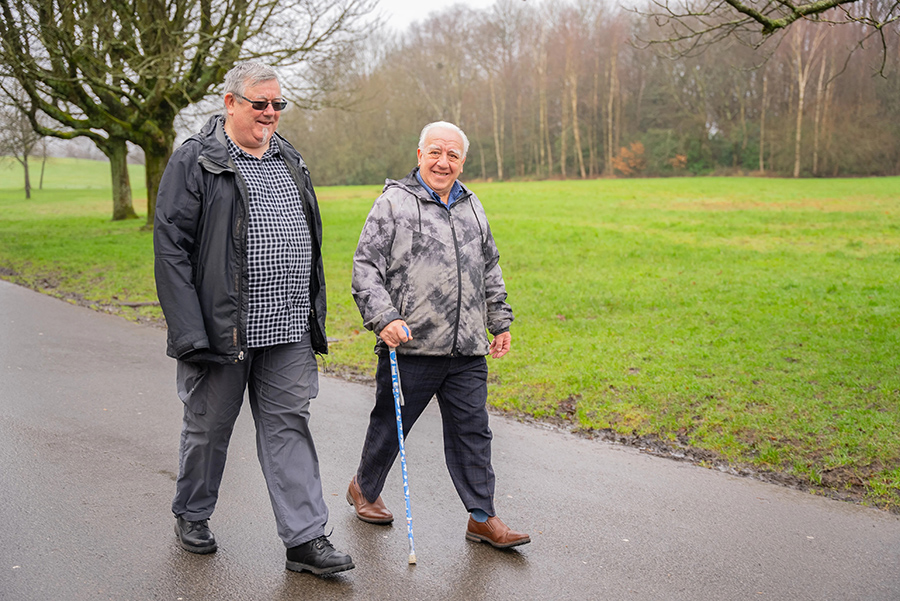

Positive self-perceptions about ageing linked to better recovery after a fall, study shows
•
A research study from Imperial College London and Coventry University has revealed that there is a strong association between an older person’s view of how they are ageing and how well they will physically recover after a fall. The study findings suggest how important psychological factors may be in post-fall physical recovery. In the…
Welcome to Assistive AI Lab Where AI Meets Inclusion
At Assistive AI Lab, we are dedicated to developing cutting-edge artificial intelligence technologies to enhance accessibility and empower individuals with diverse needs. Our interdisciplinary team passionately pursues innovative research and practical solutions, bridging the gap between advanced AI techniques and inclusive, real-world applications.
Our mission is to ensure that artificial intelligence benefits everyone, particularly those traditionally underserved by technology. By focusing on accessibility, usability, and human-centered design, our lab creates transformative tools and systems that facilitate greater independence, inclusion, and quality of life.
We specialize in:
- Assistive Technology Development: Creating intelligent solutions that improve daily living, communication, and mobility.
- Inclusive AI Systems: Ensuring AI applications are designed to be universally accessible and beneficial.
- Human-Centered Innovation: Collaborating closely with users and communities to develop meaningful, impactful technologies.
Join us in shaping a future where artificial intelligence genuinely meets the needs of all individuals, fostering a society that is truly inclusive and accessible.